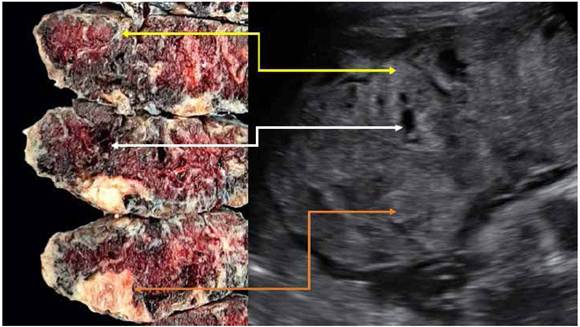
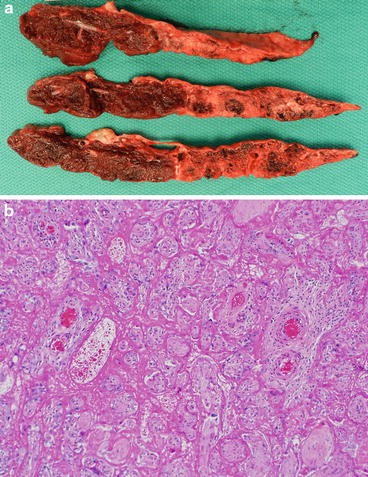
Although rare they are associated with high rates of fetal growth restriction perinatal morbidity and mortality and risks of recurrence with fetal death.
Maternal floor infarction cause.
Infant low birth weight.
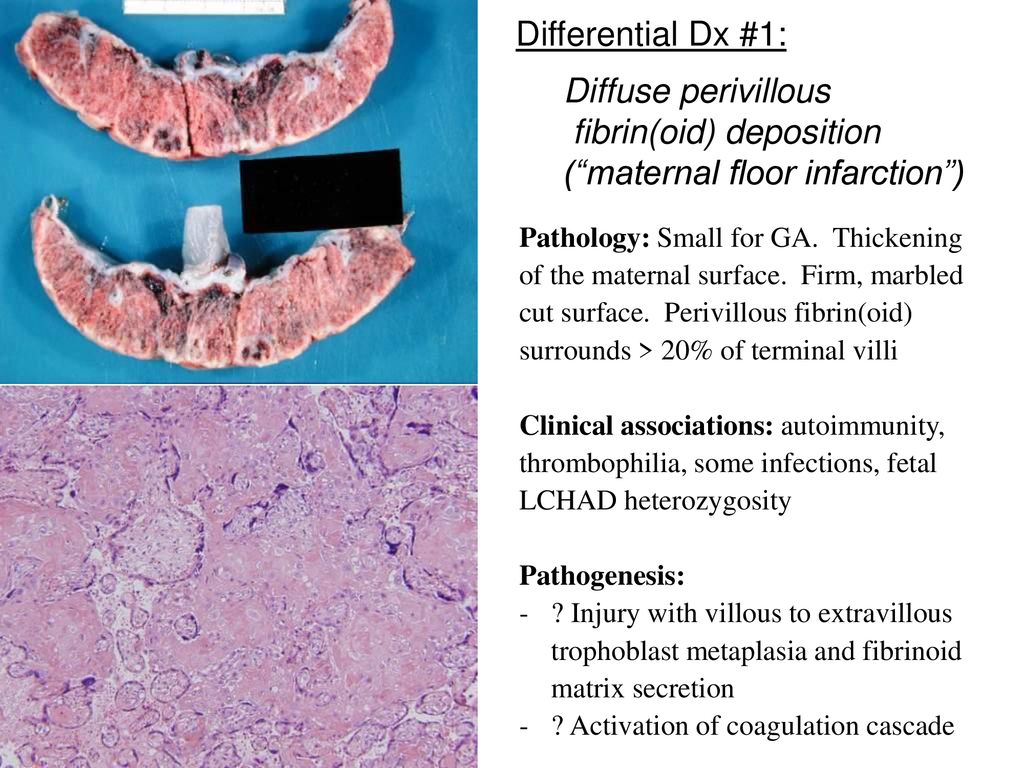
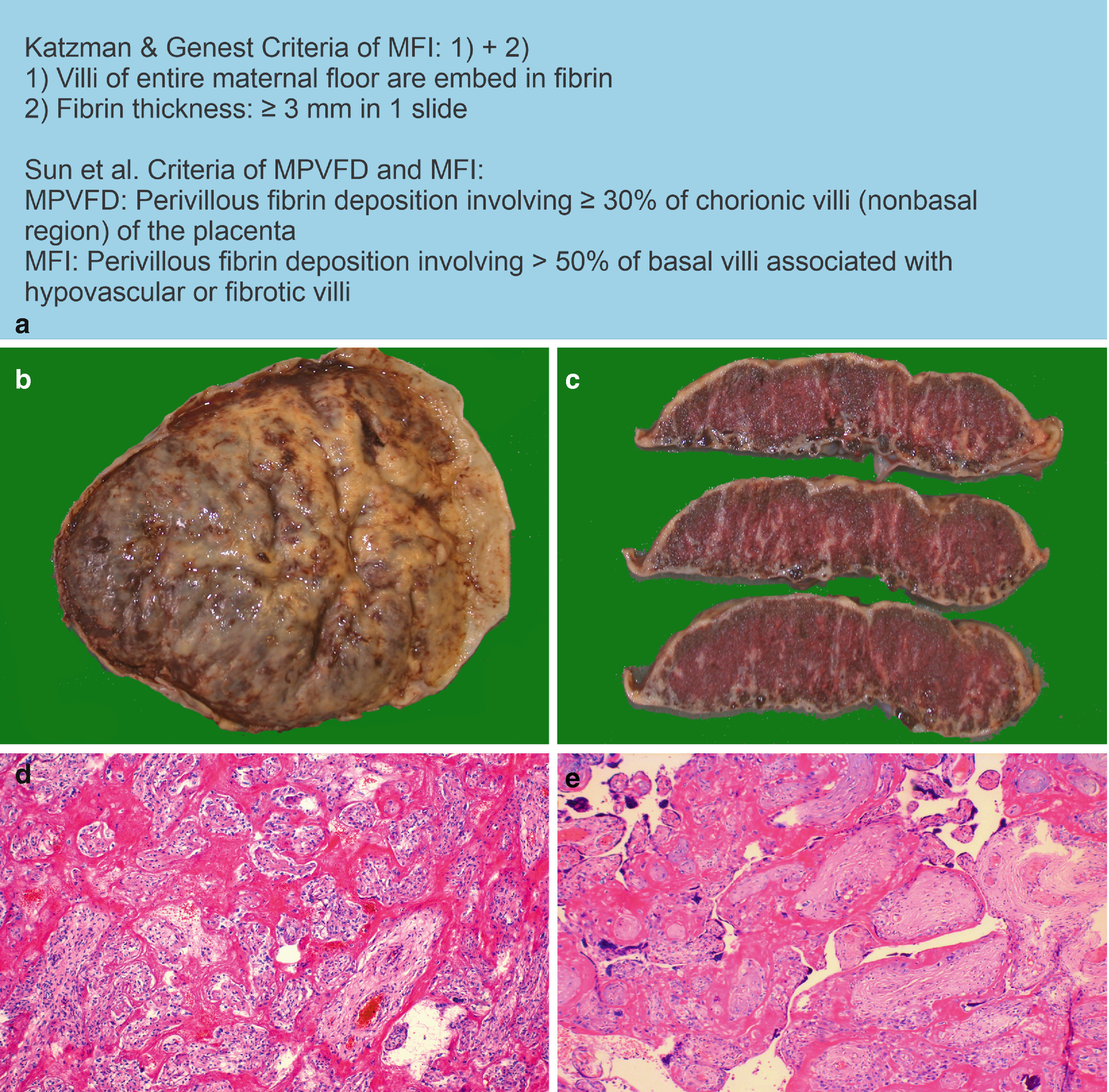
Maternal floor infarction mfi and massive perivillous fibrin deposition mpvfd are pathologically overlapping placental disorders with characteristic gross and shared light microscopic features of excessive perivillous deposition of fibrinoid material.
Sir maternal floor infarction mfi is an uncommon placental lesion associated with stillbirth and intrauterine growth retardation with an apparent high rate of recurrence in subsequent pregnancies.
3195520 pubmed indexed for medline publication types.
We report a case of booked 29 years old g3p1l1a1 who was admitted for induction of.
It is also known as massive perivillous fibrin deposition.
A rare cause of sudden intrauterine fetal demise 1.
A preventable cause of fetal death.
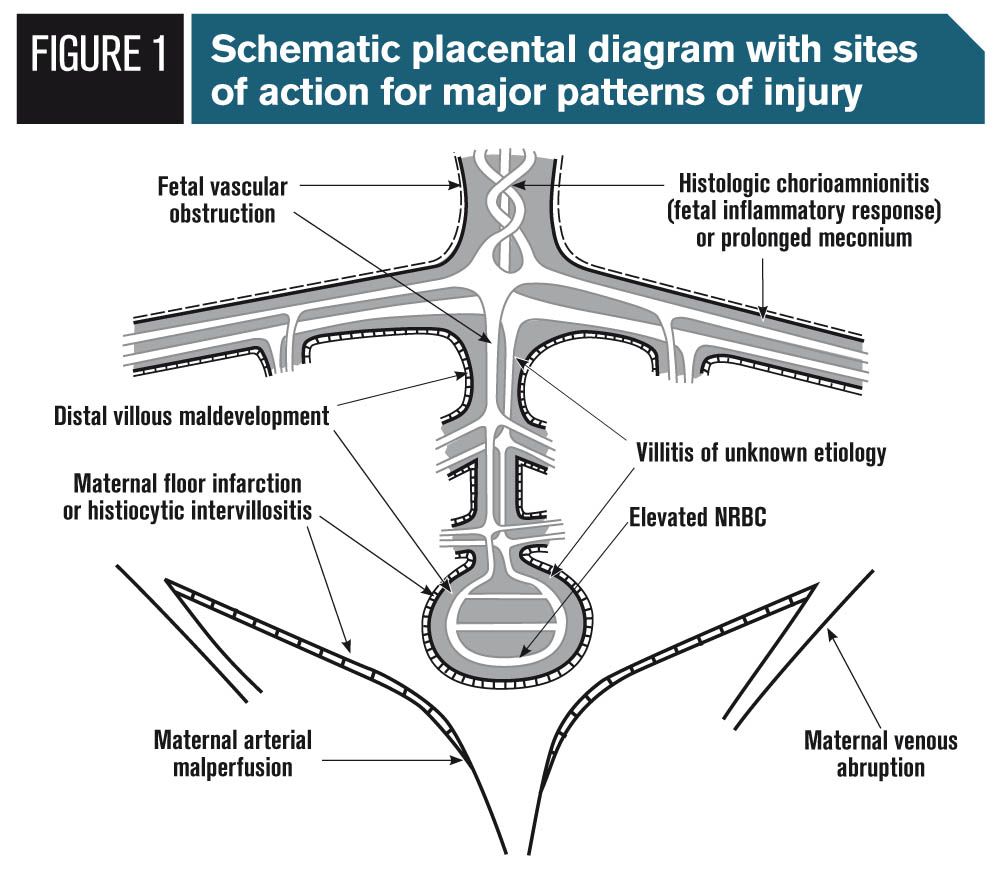
Introduction maternal floor infarction is a rare placental lesion in which large amounts of fibrin are deposited along the basal plate which becomes avascular and sclerotic.
It is formally known as placental maternal floor infarction.
Recurrent maternal floor infarction.
Am j obstet gynecol.
Maternal floor infarction is a rare placental lesion incidence 0 09 5 1 in which large amounts of.
Clewell wh manchester dk.
The term infarction is a misnomer because true placental infarcts result from arterial occlusion and ischemic necrosis of the villi.
An unusual cause of intrauterine growth retardation.
The enveloped villi become atrophic and avascular.
Maternal floor infarction maternal floor infarction abbreviated mfi is a pathology of the placenta.
Fetal growth retardation etiology fibrosis.
The disease is characterized by extensive fibrin deposition in the intervillous spaces.